@asmamstq
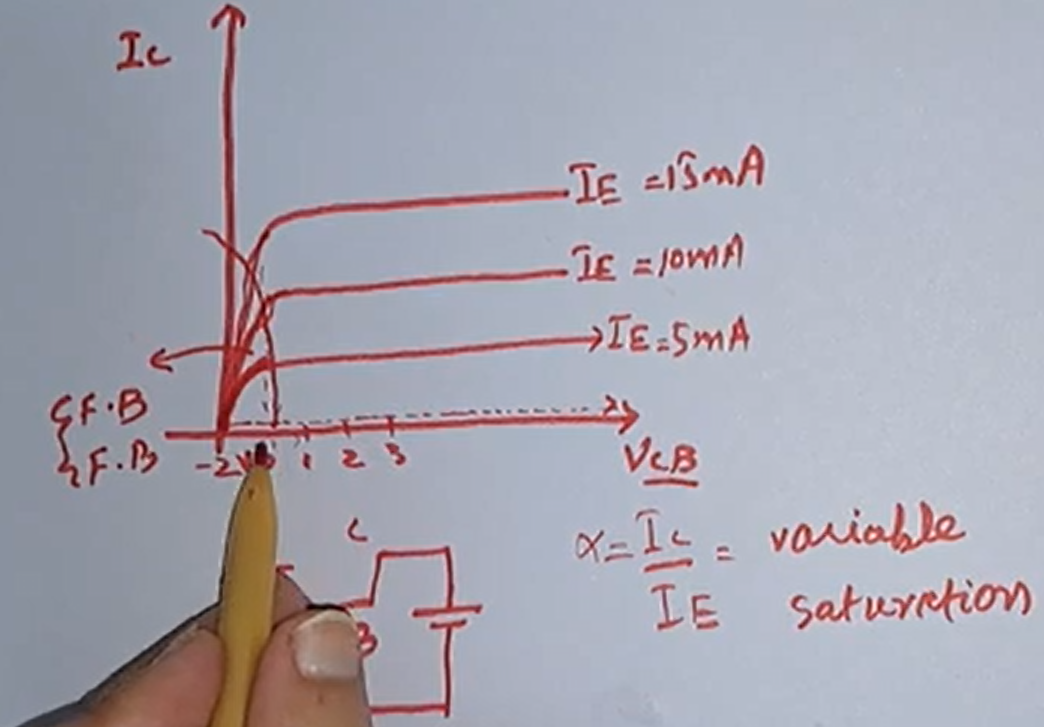
Common Base Input/Output Characteristics of BJT
Characteristics Input: The input is applied to the emitter terminal, and the input current is denoted as IE. Output: The output is taken from the collector terminal, and the output current is denoted as IC. Common Terminal: The base terminal is c…
17 Reaction
0 Comments
Report
We respect your privacy and we keep your report anonymous. You're reporting asmamstq's post
User information
- Username: asmamstq